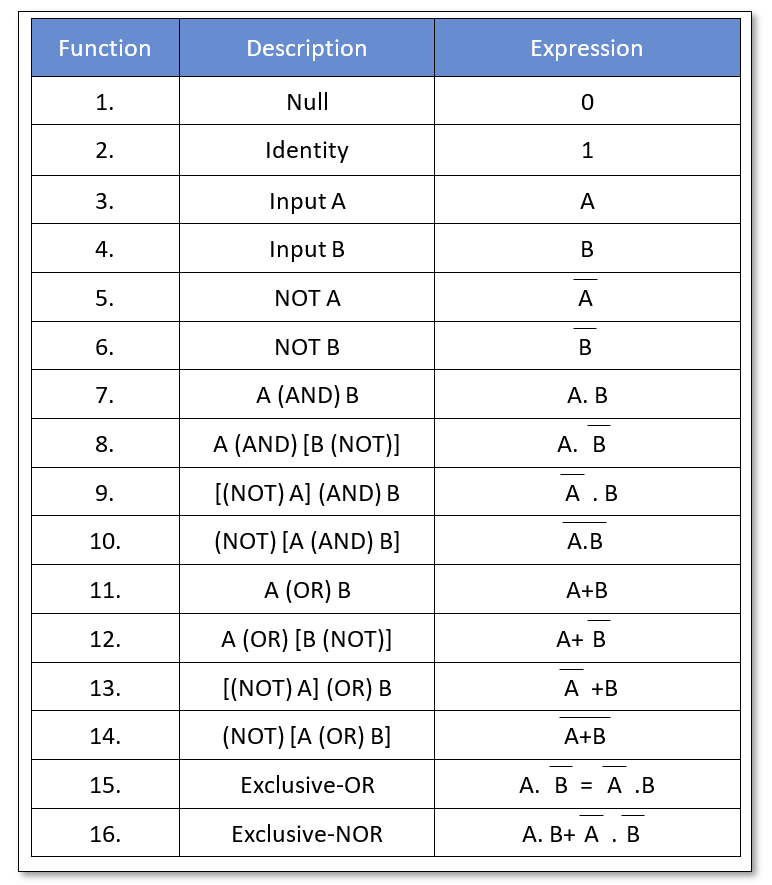
ANNULMENT LAW
The input AND’ed by ‘0’ or OR’ed by ‘1’ is stated as Annulment Law. It nullifies or diminishes the effect of the other input
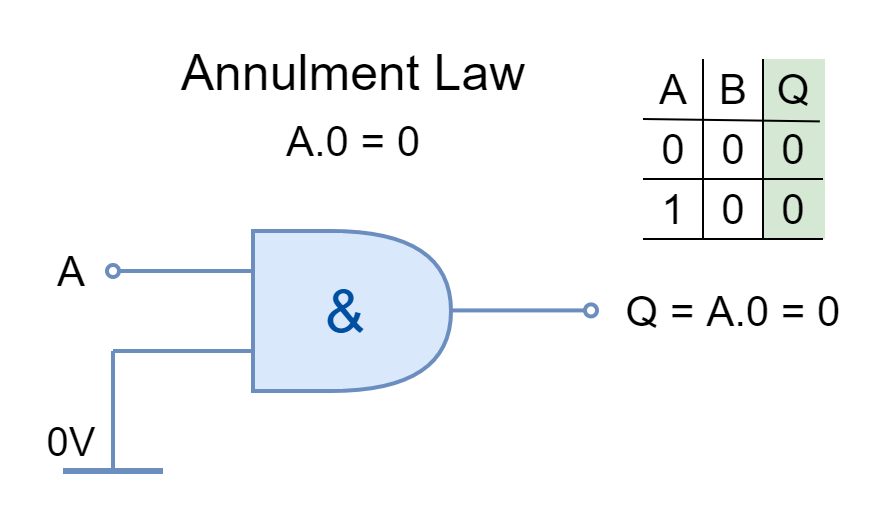
IDENTITY LAW
The input AND’ed by ‘1’ or OR’ed by ‘0’ is stated by Identity Law. It keeps the identity of the input.
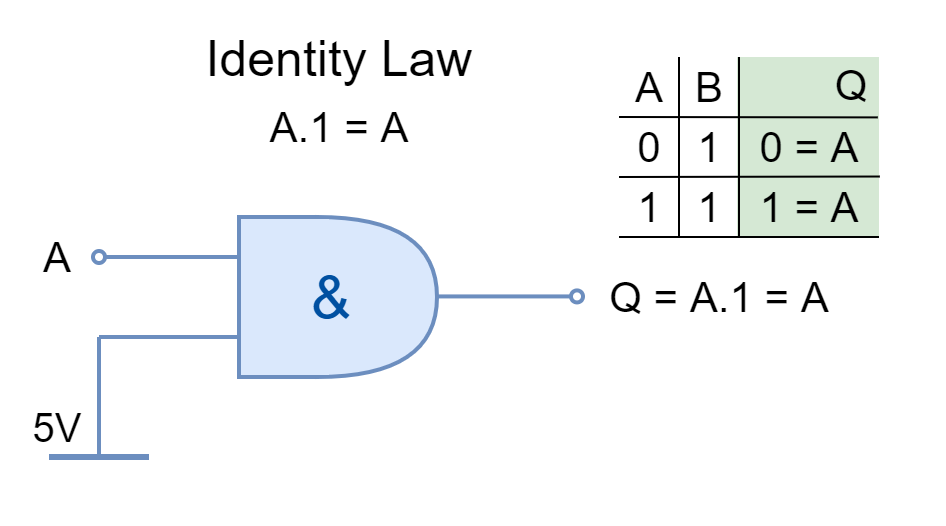
IDEMPOTENT LAW
The same inputs AND’ed or OR’ed together are stated under Idempotent Law. The logical operation can be applied multiple times without changing the result.
COMPLEMENT LAW
In Boolean Algebra, the complement is the opposite of a logical input such as ‘0’ is the complement of ‘1’ and vice versa. The input and its complement AND’ed or OR’ed together is described by Complement Law.
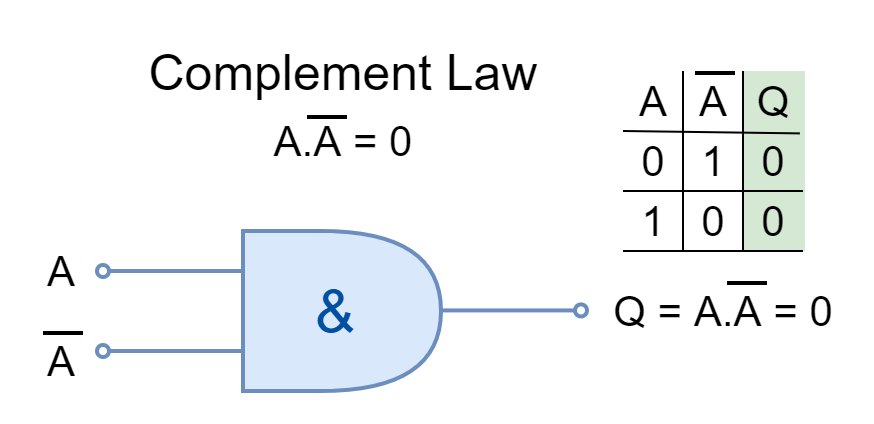
COMMUTATIVE LAW
The commutative law states that changing the order of operands (variables or inputs) does not change the result. In Boolean Algebra, the inputs can be interchanged without changing the results under commutative law.
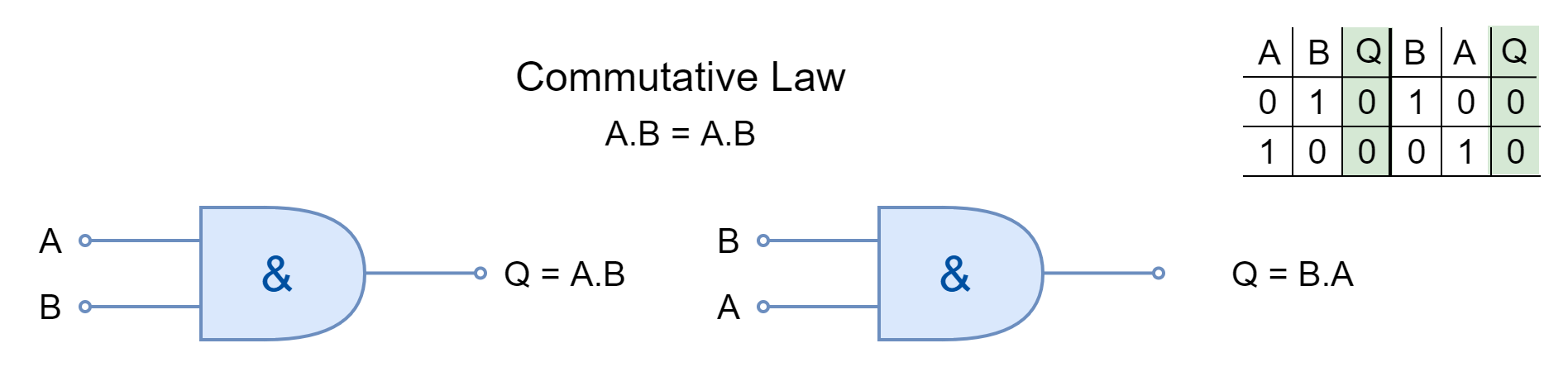
ASSOCIATIVE LAW
The associative law of multiplication states that the operands grouped differently in multiplication produce the same result. The inputs AND’ed together can be placed interchangeably to form different groups under the Associative Law.
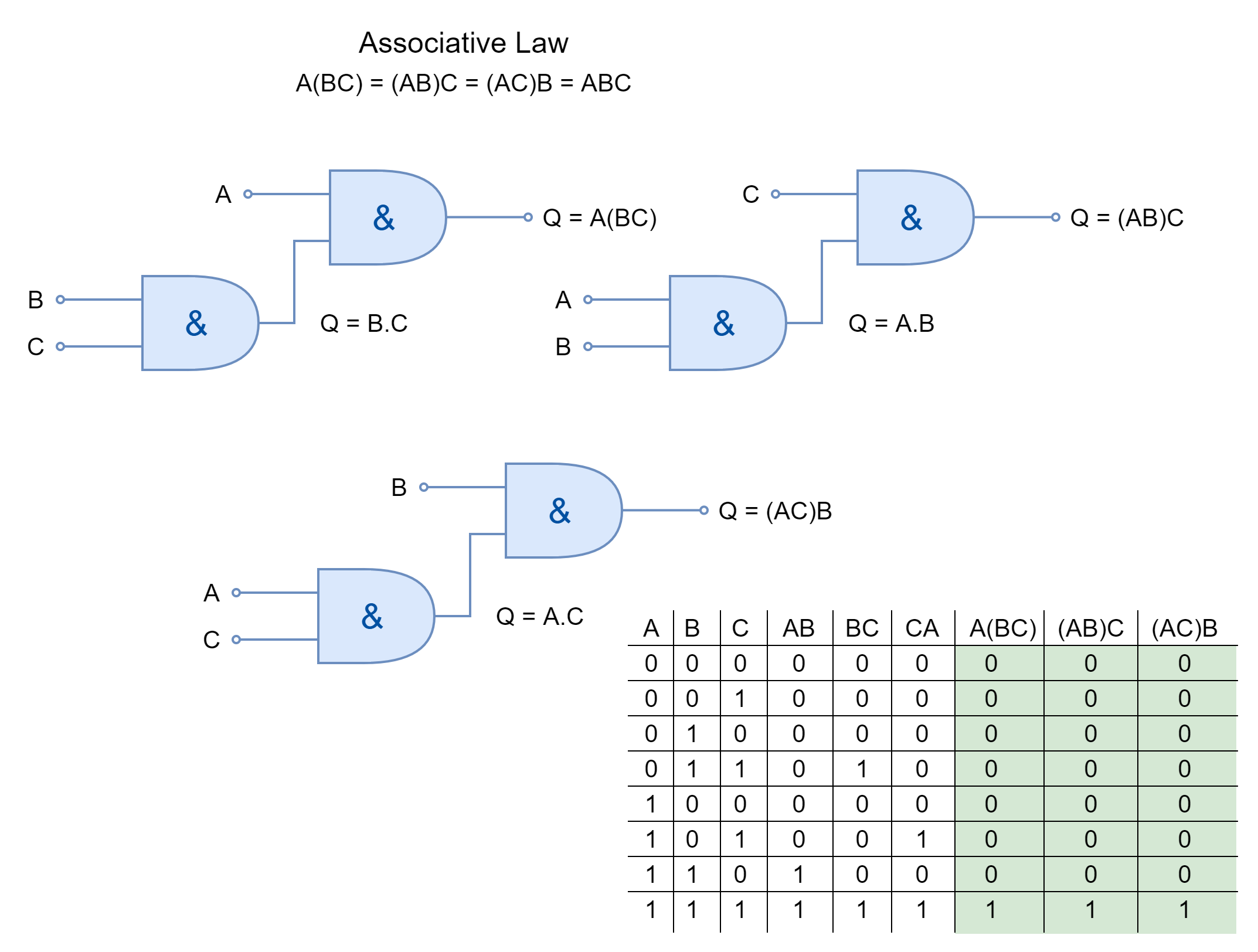
ABSORPTION LAW
Using this law, common terms are absorbed to reduce complex expressions to simpler ones.
DE MORGAN’S THEOREM
There are two De-Morgan’s theorems which are:
- The NOR of two separate terms together equals AND of individual complements of these two terms. In expression, it is stated as:
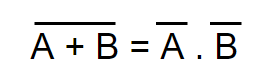
- The NAND of two separate terms together equals OR of individual complements of these two terms. In expression, it is stated as:
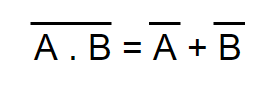
BOOLEAN POSTULATES
There are some mathematical laws that are helpful in the reduction of Boolean expressions. These Boolean postulates are listed below.
AND of 0 with itself, always equals “0”
0.0 = 0
AND of 1 with itself, always equals “1”
1.1 = 1
AND of 1 with a 0, always equals “0”
1.0 = 0
OR of 0 with itself, always equals “0”
0+0 = 0
OR of 1 with a 0, always equals “1”
1+0 = 1
OR of 1 with itself, always equals “1”
1+1 = 1
The inverse of a 0, always equal to “1”
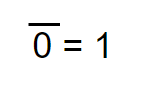
The inverse of a 1, always equal to “0”
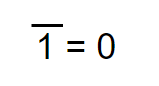
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA FUNCTIONS
The basic logic gates i.e. AND, OR, and NOT can render the following sixteen (16) Boolean functions using above stated laws, rules, theorems, etc.